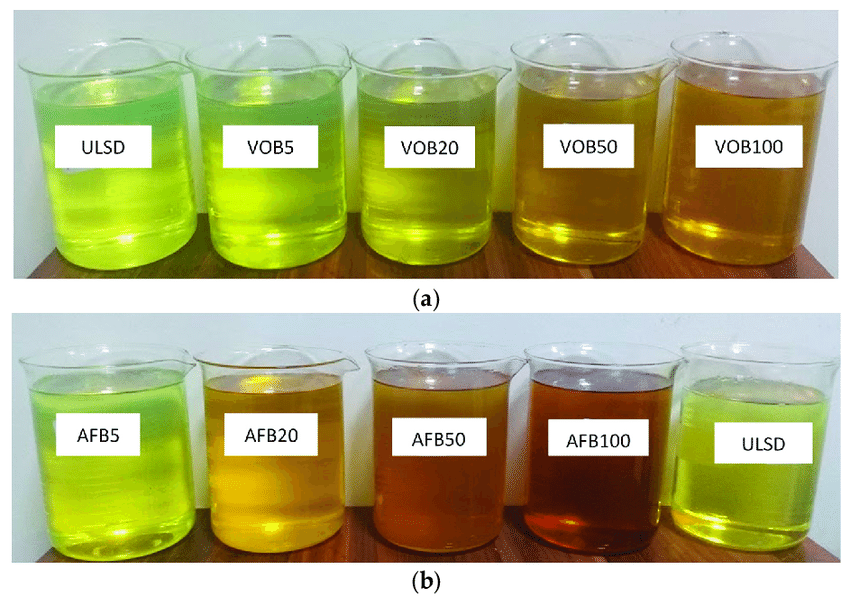
Biodiesel is a renewable, biodegradable fuel manufactured domestically from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled restaurant grease. Biodiesel meets both the biomass-based diesel and overall advanced biofuel requirement of the Renewable Fuel Standard. Renewable diesel, also called “green diesel,” is distinct from biodiesel.
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat (tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil with an alcohol, producing a methyl, ethyl or propyl ester by the process of transesterification.

E85 ethanol is used in engines modified to accept higher concentrations of ethanol. In the US such FFVs are designed to run on any mixture of gasoline or ethanol up to 85% ethanol, whereas in countries such as Brazil where the climate is typically warmer, FFV run on neat alcohol.
E85 Ethanol is a high-concentration biofuel blend which contains 51 to 83 percent ethanol, depending on location and season. E85 is meant for use in flexible fuel vehicles (FFVs), automobiles with internal combustion engines capable of supporting any ethanol blend up to E85. Unlike most lower-level blends, E85 cannot legally be used in conventional gasoline-powered vehicles.

Bio-CNG is a renewable fuel obtained by purifying biogas – in contrast to CNG, a non-renewable source of energy. Biogas is produced when microbes break down organic matter like food, crop residue, waste water, etc.
In India, Bio-CNG has immense scope, specifically as a replacement for the more widely used CNG and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Besides, bio-CNG can cater to diverse segments of the market with applications in commercial (hotels, canteens, bakeries and resorts), industrial (glass and ceramic, metal processes, cement and textiles) and automotive (public transport and private vehicles) processes.

liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), also called LP gas, any of several liquid mixtures of the volatile hydrocarbons propene, propane, butene, and butane. It was used as early as 1860 for a portable fuel source, and its production and consumption for both domestic and industrial use have expanded ever since. A typical commercial mixture may also contain ethane and ethylene, as well as a volatile mercaptan, an odorant added as a safety precaution.
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is recovered from “wet” natural gas (gas with condensable heavy petroleum compounds) by absorption. The recovered product has a low boiling point and must be distilled to remove the lighter fractions and then be treated to remove hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, and water.

Ethanol is a renewable fuel made from various plant materials collectively known as "biomass." More than 98% of U.S. gasoline contains ethanol, typically E10 (10% ethanol, 90% gasoline), to oxygenate the fuel, which reduces air pollution.
Ethanol is also available as E85 (or flex fuel), which can be used in flexible fuel vehicles, designed to operate on any blend of gasoline and ethanol up to 83%. Another blend, E15, is approved for use in model year 2001 and newer light-duty vehicles
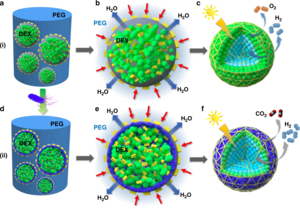
Biohydrogen is H2 that is produced biologically.[1] Interest is high in this technology because H2 is a clean fuel and can be readily produced from certain kinds of biomass. Many challenges characterize this technology, including those intrinsic to H2, such as storage and transportation of a non-condensable gas. Hydrogen producing organisms are poisoned by O2. Yields of H2 are often low
Hydrogen produced through the action of living organisms is called biohydrogen. This is a type of biofuel, like bio-ethanol, bio-diesel or bio-gas or bio-oil. There are three classes of biofuels:-

Synthetic lubricants are not usually recommended by gear manufacturers for general gear applications due to high cost, limited availability, and lack of knowledge of their properties. Nevertheless, they are used with good success in applications with extremely high or low temperatures, where fire protection is required, or where very high speeds or high wear rates are encountered. The user must be careful when selecting these lubricants since some of them remove paint and attack rubber seals. The new synthesized hydrocarbons (SHC) have many desirable features such as compatibility with mineral oils and excellent high and low temperature properties. They are excellent selections when EP lubricants along with high temperature operation are required.